💧 Lesson 1: Liquidity Infrastructure – AMMs & Hybrids
This lesson dives into DeFi liquidity infrastructure, focusing on Automated Market Makers (AMMs) and their evolution into hybrid models. AMMs are decentralized protocols that allow users to swap tokens without centralized intermediaries, forming the foundation of most DeFi platforms. As the space evolves, hybrid models are emerging to enhance efficiency and scalability while offering traders greater control and better pricing.
🔍 Overview
Liquidity is the lifeblood of any financial market. In decentralized finance, AMMs automate the process of price discovery and trade execution, allowing users to swap assets without traditional intermediaries. Hybrid models extend this framework by integrating order books, dynamic pricing, and routing mechanisms to improve capital efficiency and user experience.
📋 What You’ll Need to Know
- Prerequisites: Solid understanding of blockchain fundamentals, AMMs, and DeFi basics.
- Target Audience: DeFi developers, protocol designers, analysts, and DeFi users.
🎯 Learning Objectives
- Understand how AMMs function and their importance in DeFi
- Identify key AMM types (constant product, curve-based, hybrid)
- Explore liquidity provisioning and impermanent loss
- Evaluate the advantages and limitations of hybrid DEX models
- Recognize the innovations shaping next-generation liquidity layers
✍️ Content
🔄 What is an AMM?
To understand how liquidity pools operate, it’s helpful to first explore the basics of Automated Market Makers (AMMs). AMMs are a type of decentralized exchange (DEX) that use mathematical formulas and smart contracts to enable cryptocurrency trading. These platforms run continuously and allow users to swap digital assets directly from their wallets, without the need for traditional brokers or centralized order books.
An Automated Market Maker (AMM) is a smart contract protocol that facilitates token swaps using liquidity pools instead of traditional buyers and sellers.
- Users trade directly against a pool of tokens.
- Liquidity Providers (LPs) deposit pairs of tokens and earn a share of trading fees.
- Pricing is determined algorithmically using a formula like x * y = k (Uniswap V2).
This innovation democratized liquidity provision and catalyzed DeFi’s exponential growth.
💧 The Concept of Liquidity Pools
Let’s now take a closer look at liquidity pools. Unlike traditional markets that rely on order books to match buyers and sellers, AMMs use liquidity pools to process trades. These pools are created when users deposit pairs of tokens into a smart contract, forming a shared reserve of assets. Traders then interact with this pool to swap tokens, eliminating the need for centralized intermediaries or matching engines.
How Liquidity Pools Function
At the heart of liquidity pools is the participation of Liquidity Providers (LPs), who supply pairs of tokens to decentralized pools. Instead of matching buyers and sellers like in traditional finance, AMMs allow traders to swap assets directly with these pooled funds. The smart contract algorithm determines the exchange rate dynamically, depending on the pool’s current token balances. Each transaction adjusts the pool’s reserves, which in turn influences the pricing for future trades. This model ensures continuous availability of liquidity without relying on counterparties.
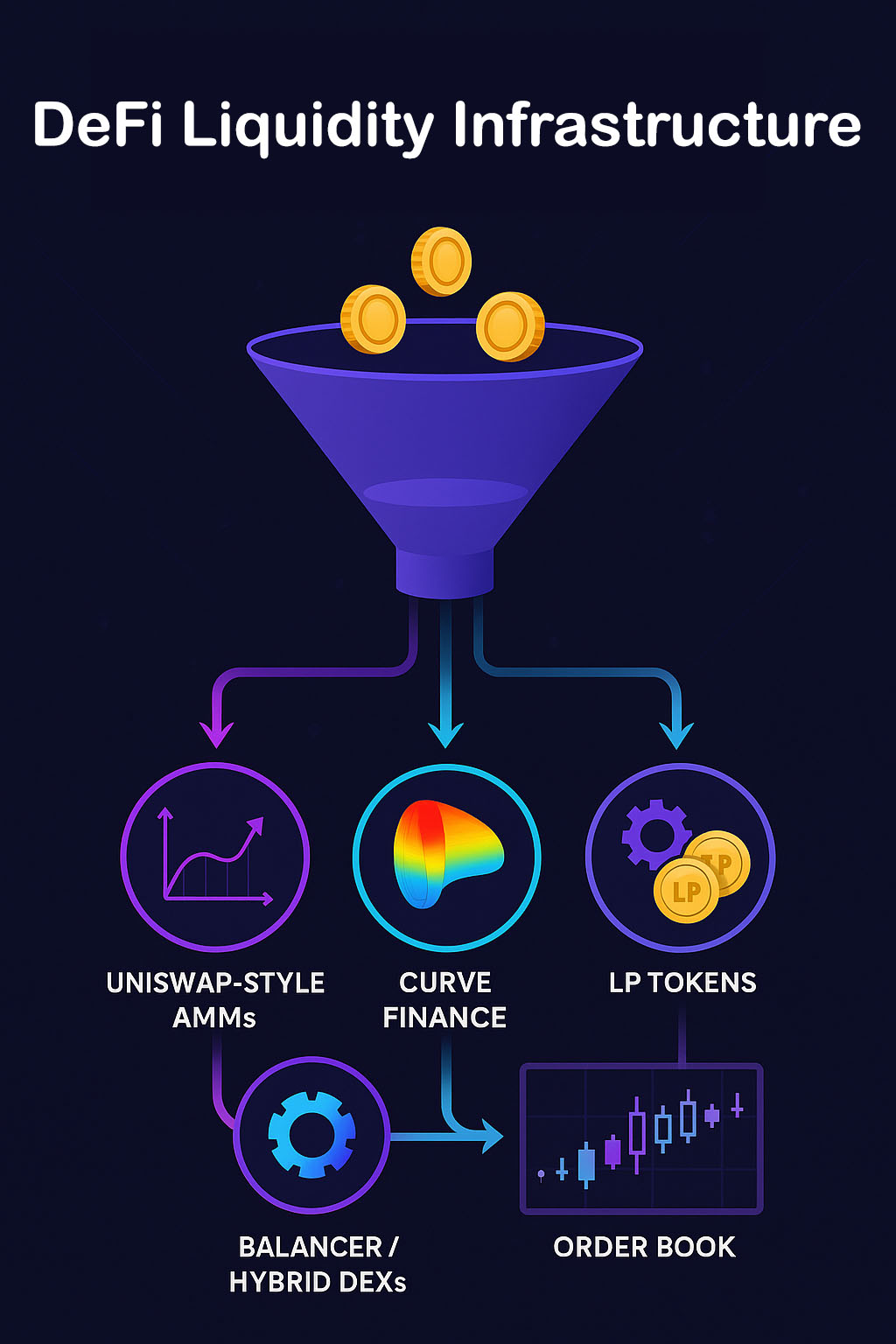
⚙️ Types of AMM Models
1.Constant Product AMMs
- Formula:
x * y = k - Used by: Uniswap, Sushiswap
- Simple, but suffers from high slippage on large trades
2.StableSwap AMMs
- Curve-based model optimized for stablecoins
- Used by: Curve Finance
- Provides low-slippage swaps between similarly priced assets
3.Dynamic AMMs
- Adjust fee tiers, weightings, and routing logic in real time
- Used by: Balancer, Kyber Dynamic Market Maker
- Improves capital efficiency and supports custom liquidity configurations.
🔀 Hybrid DEX Architectures
Hybrid models combine AMM logic with traditional order books or routing engines, bridging the gap between DeFi and CeFi experiences.
Examples:
- dYdX: Off-chain order book + on-chain settlement
- Injective: Fully decentralized order book with custom matching logic
- CowSwap: Batch auction model to prevent MEV and ensure fair pricing
Benefits include:
- Better pricing for high-volume trades
- Greater control for professional traders
- Reduced slippage and front-running
💼 Liquidity Providers & Risks
Providing liquidity isn’t without risk:
- Impermanent Loss: Occurs when asset prices diverge from when LPs entered the pool
- Volatility Exposure: LPs can lose more compared to holding assets outright
- Pool Fragmentation: Too many similar pools dilute capital
Mitigation strategies:
- Use stablecoin pairs (less price divergence)
- Opt for protocols with dynamic fee adjustment
- Participate in protocols offering IL protection (e.g., Bancor v3).
🌊 The Evolution of Liquidity Infrastructure
AMMs are evolving to become more capital-efficient, customizable, and composable:
- Concentrated Liquidity: (Uniswap v3) lets LPs provide liquidity within specific price ranges
- Composable Pools: Balancer enables multi-token pools with adjustable weights
- Routing Optimization: Aggregators like 1inch and Matcha ensure best-price execution across DEXs.
These innovations enhance the user experience and attract institutional capital.
✨ Key Elements
- AMM formulas and curve logic
- LP tokens and yield farming
- Slippage and impermanent loss
- Hybrid order book integrations
- Liquidity aggregation and routing
 Related Terms:
Related Terms:
- Constant Product Formula
- Slippage Tolerance
- LP Token
- Price Impact
- TWAP (Time-Weighted Average Price)
- On-chain Settlement
- Sandwich Attacks
- MEV (Miner Extractable Value)
- Concentrated Liquidity
📌 Conclusion
AMMs revolutionized finance by replacing order books with programmable liquidity pools, allowing anyone to become a market maker. As the DeFi landscape matures, hybrid models bring deeper liquidity, more efficient markets, and enhanced usability. Understanding these mechanics is crucial for navigating DeFi protocols and capitalizing on opportunities with confidence.
Featured Courses
Capstone: Simulated Web3 Journey
Managing Risks & Red Flags in Web3
Privacy & Transaction Optimization
Using Crypto in Daily Life
NFTs & Web3 Apps in Practice
Introduction to DeFi: Lending, Staking & Yield Explained
Understanding Block Explorers in Crypto
Bridges & Multi-Chain Navigation
Swapping Tokens & Using DEXs
🚀 Ready for the Next Level?
Scale deeper into DeFi by understanding how derivatives bring leverage, hedging, and complex financial instruments into decentralized ecosystems. Let’s break down perpetuals, options, and synthetic assets next.
Start Lesson 2 – DeFi Derivatives ExplainedJoin the Crypto Hoopoe Community

 Related Terms:
Related Terms: